PHP Compound Types PHP
- PHP Tutorial
- What is PHP
- Install PHP
- PHP Example
- PHP Echo
- PHP Print
- PHP Variables
- PHP $ and $$ Variables
- PHP Constants
- Magic Constants
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Operators
- PHP Comments
- PHP Boolean
- PHP is_bool() function
- PHP Integer
- PHP is_int() function
- PHP Float
- PHP is_float Function
- PHP Compound Types
- PHP Special Types
- PHP is_null() function
- PHP If Else
- PHP Switch
- PHP For Loop
- PHP While Loop
- PHP do while loop
- PHP Break
- PHP Functions
- PHP Parameterized Function
- PHP Call By Value
- PHP Call By Reference
- PHP Default Argument Values Function
- PHP Variable Length Argument Function
- PHP Recursive Function
- PHP Arrays
- PHP Indexed Array
- PHP Associative Array
- PHP Multidimensional Array
- PHP Array Functions
- PHP String
- PHP String Functions
- PHP Math functions
- PHP Form Handling | GET and POST method
- PHP Include File
- PHP Cookie
- PHP Session
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Read File
- PHP Write File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Download File
- PHP Mail
- PHP MySQL Connect
- PHP MySQL Create Database
- PHP MySQL Create Table Example
- PHP MySQL Insert Record
- PHP Prepared Statements
- PHP MySQL Update Record
- PHP MySQL Delete Record
- PHP MySQL Select
- PHP MySQL Order By
- PHP Limit Data MySql
- PHP JSON
- PHP XML Parsers
- PHP SimpleXML Parser
- PHP SimpleXML - Get Node/Attribute Values
- PHP XML Expat Parser
- PHP XML DOM Parser
- PHP - AJAX intro
- MySQL CREATE VIEW
PHP Compound Types
PHP Compound Types
There are 2 compound data types in PHP.
Array:
The array is a collection of heterogeneous (dissimilar) data types. PHP is a loosely typed language that?s why we can store any type of values in arrays.
Normal variable can store single value, array can store multiple values.
The array contains a number of elements, and each element is a combination of element key and element value.
SYNTAX OF ARRAY DECLARATION:
- Variable_name = array (element1, element2, element3, element4......)
Example 1
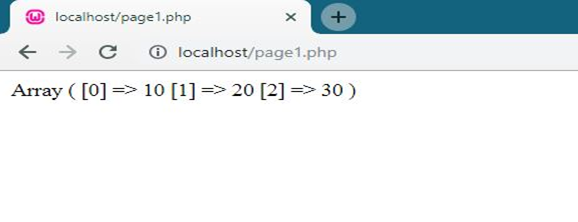
- <?php
- $arr= array(10,20,30);
- print_r($arr);
- ?>
Example 2
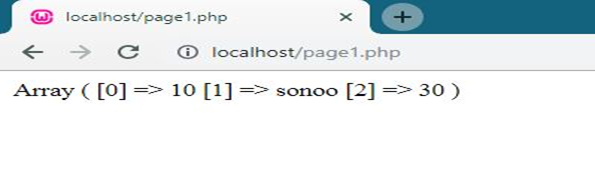
- <?php
- $arr= array(10,'sonoo',30);
- print_r($arr);
- ?>
Example 3
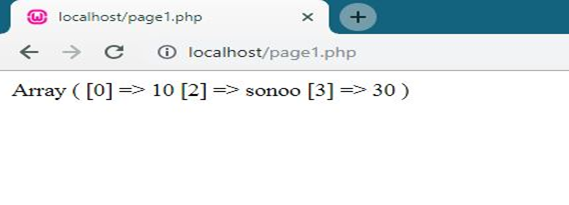
- <?php
- $arr= array(0=>10,2=>'sonoo',3=>30);
- print_r($arr);
- ?>
Object:
An object is a data type which accumulates data and information on how to process that data. An object is a specific instance of a class which delivers as templates for objects.
SYNTAX:
At first, we must declare a class of object. A class is a structure which consists of properties and methods. Classes are specified with the class keyword. We specify the data type in the object class, and then we use the data type in instances of that class.
Example 1
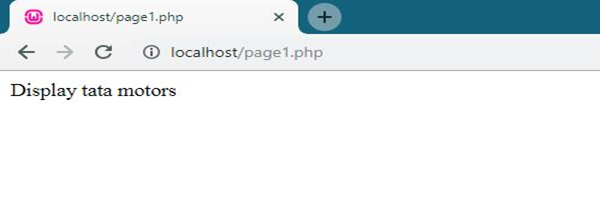
- <?php class vehicle
- {
- function car()
- {
- echo "Display tata motors";
- }
- }
- $obj1 = new vehicle;
- $obj1->car();
- ?>
Example 2
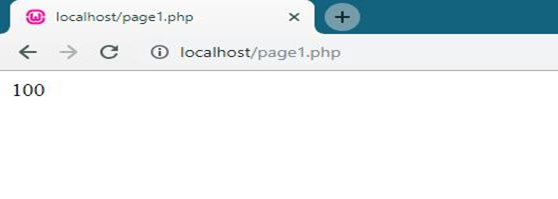
- <?php
- class student
- {
- function student()
- {
- $this->kundan = 100;
- }
- }
- $obj = new student();
- echo $obj->kundan;
- ?>
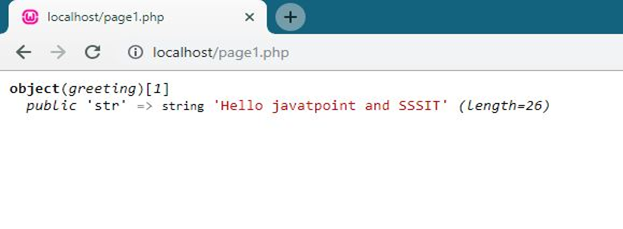
Example 3
- <?php
- class greeting
- {
- public $str = "Hello javatpoint and SSSIT";
- function show_greeting()
- {
- return $this->str;
- }
- }
- $obj = new greeting;
- var_dump($obj);
- ?>
Source : JavaTPoint




